Trauma Awareness Month and vRad’s Impact
As I mentioned in my last post, May is both Trauma and Stroke Awareness month. vRad serves hundreds of trauma and stroke centers across the U.S. The...

Remote radiologist jobs with flexible schedules, equitable pay, and the most advanced reading platform. Discover teleradiology at vRad.

Radiologist well-being matters. Explore how vRad takes action to prevent burnout with expert-led, confidential support through our partnership with VITAL WorkLife. Helping radiologists thrive.

Visit the vRad Blog for radiologist experiences at vRad, career resources, and more.

vRad provides radiology residents and fellows free radiology education resources for ABR boards, noon lectures, and CME.

Teleradiology services leader since 2001. See how vRad AI is helping deliver faster, higher-quality care for 50,000+ critical patients each year.

Subspecialist care for the women in your community. 48-hour screenings. 1-hour diagnostics. Comprehensive compliance and inspection support.

vRad’s stroke protocol auto-assigns stroke cases to the top of all available radiologists’ worklists, with requirements to be read next.

vRad’s unique teleradiology workflow for trauma studies delivers consistently fast turnaround times—even during periods of high volume.

vRad’s Operations Center is the central hub that ensures imaging studies and communications are handled efficiently and swiftly.

vRad is delivering faster radiology turnaround times for 40,000+ critical patients annually, using four unique strategies, including AI.
.jpg?width=1024&height=576&name=vRad-High-Quality-Patient-Care-1024x576%20(1).jpg)
vRad is developing and using AI to improve radiology quality assurance and reduce medical malpractice risk.

Now you can power your practice with the same fully integrated technology and support ecosystem we use. The vRad Platform.

Since developing and launching our first model in 2015, vRad has been at the forefront of AI in radiology.

Since 2010, vRad Radiology Education has provided high-quality radiology CME. Open to all radiologists, these 15-minute online modules are a convenient way to stay up to date on practical radiology topics.

Join vRad’s annual spring CME conference featuring top speakers and practical radiology topics.

vRad provides radiology residents and fellows free radiology education resources for ABR boards, noon lectures, and CME.

Academically oriented radiologists love practicing at vRad too. Check out the research published by vRad radiologists and team members.

Learn how vRad revolutionized radiology and has been at the forefront of innovation since 2001.

%20(2).jpg?width=1008&height=755&name=Copy%20of%20Mega%20Nav%20Images%202025%20(1008%20x%20755%20px)%20(2).jpg)

Visit the vRad blog for radiologist experiences at vRad, career resources, and more.


Explore our practice’s reading platform, breast imaging program, AI, and more. Plus, hear from vRad radiologists about what it’s like to practice at vRad.

Ready to be part of something meaningful? Explore team member careers at vRad.

May is both Stoke and Trauma awareness month. In recognition of this, we will be publishing a series of 3 posts covering:
Each May, the American Stroke Association, the National Stroke Association and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) work to promote stroke awareness. We’d like to take this opportunity to join them in raising awareness of stroke, and share the work that we do to support stroke centers and patients across the nation.
vRad is proud to provide radiology service to approximately 30% of the hospitals across the U.S. Our busiest times are the middle of night, weekends and holidays. If you or a loved one are exhibiting signs of a stroke in the middle of the night and rush to the closest emergency room – it’s very possible your Head CT scan is being read by a vRad board-certified radiologist.
A stroke can happen to anyone, at any age, and at any time. In fact, in the U.S., someone has a stroke every 40 seconds. It’s the fifth leading cause of death – yet up to 80 percent of strokes are preventable. With stroke treatment, every second counts – and the first step in treating stroke is to identify when a potential stroke is occurring. The most common method to quickly identify a potential stroke is the acronym FAST—which stands for FACE, ARMS, SPEECH and TIME—as shown below:
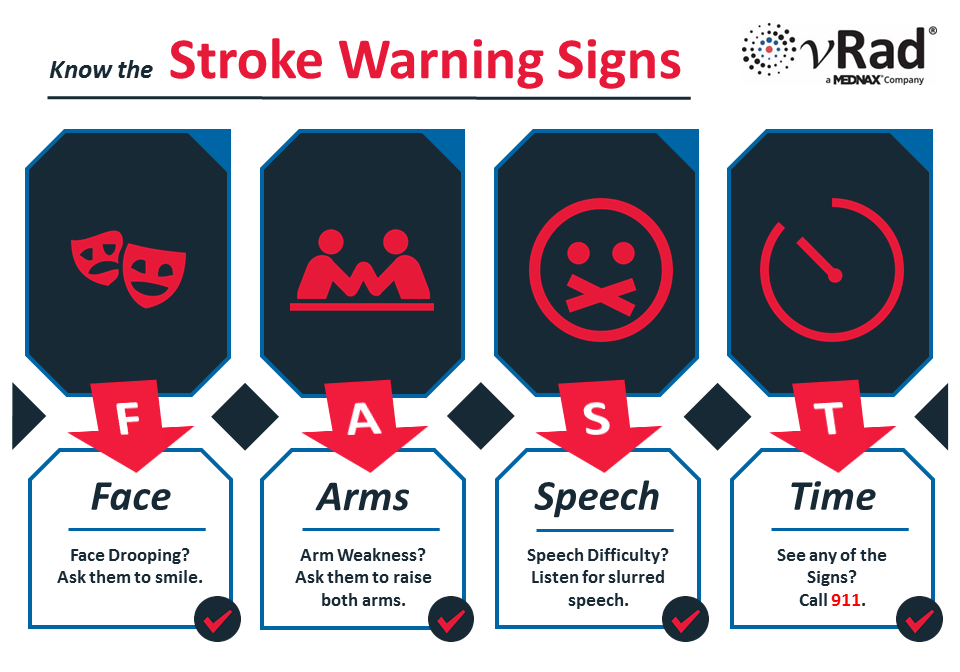
Here’s a downloadable copy you can share or print as a reminder.
What is a Stroke?
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to your brain is interrupted or reduced. This deprives your brain of oxygen and nutrients, which can cause your brain cells to die.
A stroke may be caused by a blocked artery (ischemic stroke) or the leaking or bursting of a blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke). Some people may experience only a temporary disruption of blood flow to their brain (transient ischemic attack, or TIA).
What is a Stroke Protocol in Radiology?
A stroke protocol exam in radiology is the rapid response imaging of the CT Head to quickly diagnose and administer treatment.
Referred to as the “Golden Hour,” the first hour the patient begins exhibiting the signs and symptoms of a stroke is critical. The key concept to remember is the clock starts ticking as soon as signs and symptoms appear—not when you arrive at the stroke center or emergency department! If correctly diagnosed and treated quickly, the patient can fully recover, but delayed treatment can have dire consequences for patient outcomes. When caring for stroke patients Time is Brain!
Stroke Timeline Expectations:
vRad’s Impact on Stroke Patients Nationwide
As a trusted partner across hundreds of stroke centers nationwide, vRad has extraordinary performance expectations. To deliver on these expectations, vRad built an internal Stroke Protocol workflow that ensures the following:
Since 2012, vRad’s Average Stroke Protocol Turn-Around-Time (TAT) for CT Head = 6.73 minutes.
In 2015, we extended access to our “Stroke Protocol” urgency to all facilities (not just stroke centers) to ensure the standard of care across rural facilities was escalated and expedited for any patients suspected of stroke. Treating a patient within the “Golden Hour” is critical.
Within one year of extending the Stroke Protocol urgency to all facilities, we increased the number of stroke patients we cared for by over 2,000 per month and continue to demonstrate excellent TAT results.
2016 Stroke Protocol Performance Highlights
vRad Stroke Protocol is available for CT Head and CTA Head and Neck exams.
Improving our internal protocols and client partnerships is a passion across our Operations Team, and vRad as a whole. Cross-functional collaboration allows us to define and understand complex problems and implement effective solutions. In the case of stroke protocol, we continue to challenge ourselves to further improve the rapid delivery of exceptional patient care.
Next week we’ll be discussing our Trauma Protocol in honor of Trauma Awareness Month – stay tuned!
Joe Schmugge
About the Author
Back to Blog
As I mentioned in my last post, May is both Trauma and Stroke Awareness month. vRad serves hundreds of trauma and stroke centers across the U.S. The...
A growing number of health organizations are making computed tomographic perfusion (CTP) a critical part of their stroke intervention protocols.

Today is our third and final post in deference to Stroke and Trauma Awareness Month:
vRad (Virtual Radiologic) is a national radiology practice combining clinical excellence with cutting-edge technology development. Each year, we bring exceptional radiology care to millions of patients and empower healthcare providers with technology-driven solutions.
Non-Clinical Inquiries (Total Free):
800.737.0610
Outside U.S.:
011.1.952.595.1111
3600 Minnesota Drive, Suite 800
Edina, MN 55435